Genome editing has taken a significant leap forward with the development of a new web-based tool that improves the accuracy of CRISPR technology by identifying off-target effects across genetic variations. This breakthrough, led by Professor Jeongbin Park of Pusan National University, was published in the journal Nucleic Acids Research on May 8, 2025.
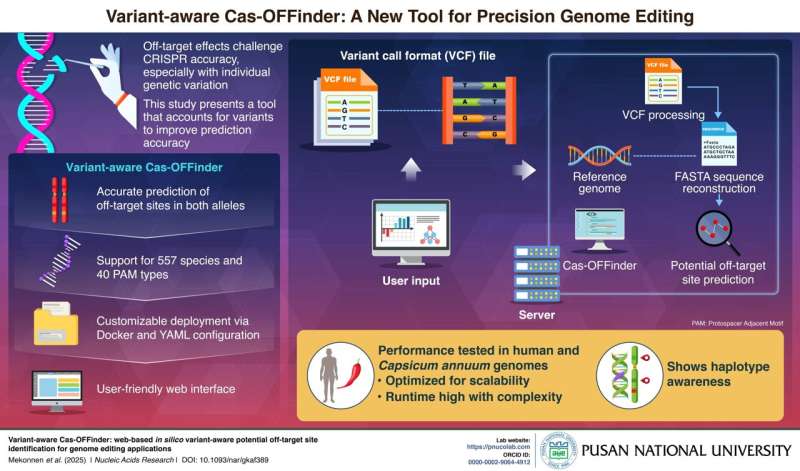
The tool, known as Variant-aware Cas-OFFinder, addresses a critical challenge in genome editing: unintended edits at off-target DNA sites. These off-target effects can lead to harmful mutations and are notoriously difficult to predict due to the unique genetic makeup of each organism. Traditional prediction tools often rely on a standard reference genome, overlooking individual genetic differences such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions, and deletions.
Innovative Approach to Genome Editing
Variant-aware Cas-OFFinder represents a significant advancement by incorporating genetic diversity directly into off-target predictions. The tool accepts phased single-sample VCF files and supports GPU acceleration, facilitating applications beyond standard model organisms. By reconstructing allele-specific genome sequences, it performs haplotype-level analysis, providing a more detailed and accurate picture of potential off-target effects.
“In my view, genome editing tools should be as individualized as the genomes they target,” says Prof. Park. “Our tool lays the groundwork for more accurate and personalized editing strategies.”
Testing and Results
The research team, including co-first authors Abyot Melkamu Mekonnen and Kang Seong, tested the tool on human and sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum) genomes using public and cultivar-specific sequencing data. In humans, the tool revealed off-target sites on chromosome 10 that were absent from the standard reference genome. In sweet pepper, it identified distinct allele-specific off-targets, which could be instrumental for plant breeding.
Compared to existing tools such as Cas-OFFinder and CRISPRitz, Variant-aware Cas-OFFinder consistently identified unique off-targets caused by small variants like insertions and deletions. Although it does not yet detect large structural variants, the tool supports 557 species and 40 PAM types, and is fully customizable through YAML files.
Implications for Medicine and Agriculture
“Precision genome editing requires precision tools,” remarks Prof. Park. “We believe Variant-aware Cas-OFFinder will play a central role in developing safer, more effective CRISPR therapies and agricultural applications.”
The tool is available as a user-friendly web interface and a command-line version, with its source code, benchmark tools, and example datasets freely accessible on GitHub and Zenodo. While its haplotype-level analysis may slow performance slightly compared to earlier tools, this trade-off enables greater accuracy and reliability in genome editing research.
Looking Ahead
The introduction of Variant-aware Cas-OFFinder marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of genome editing technologies. By addressing the variability inherent in genetic makeup, this tool enhances the precision of CRISPR applications, paving the way for more personalized and effective interventions in both medicine and agriculture.
As genome editing continues to evolve, tools like Variant-aware Cas-OFFinder will be essential in ensuring that the potential of CRISPR technology is fully realized while minimizing risks associated with off-target effects. The research community and industry stakeholders will likely keep a close watch on further developments and improvements in this promising field.
More information: Abyot Melkamu Mekonnen et al, Variant-aware Cas-OFFinder: web-based in silico variant-aware potential off-target site identification for genome editing applications, Nucleic Acids Research (2025). DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf389