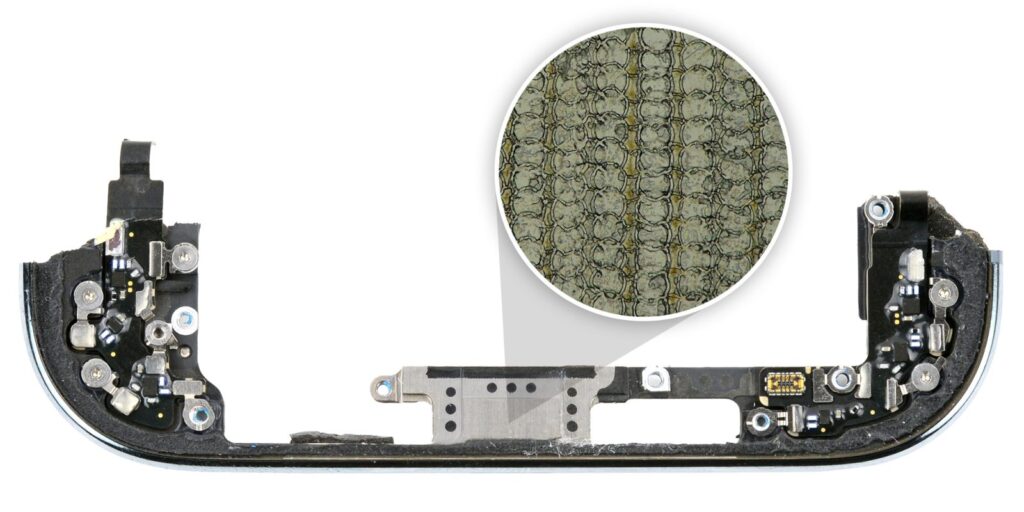
Apple’s recent unveiling of its 3D printing process for the Apple Watch Series 11 and Ultra 3 has prompted further investigation into its innovative manufacturing techniques. In a detailed teardown of the iPhone Air, iFixit has provided insights into the device’s 3D-printed USB-C port, revealing surprising findings that challenge previous assumptions about the technology used.
According to iFixit’s analysis, the USB-C port does not employ the binder jetting technique, as previously reported. Instead, it appears that Apple has utilized a method discussed in a medical study published six years ago. This study emphasizes the advantages of creating structures between 10 to 50 micrometers on titanium surfaces through pulsed laser ablation. This technique is known for its ability to introduce anti-bacterial properties in prosthetics. Although the iPhone Air’s USB-C port lacks these anti-bacterial features, it seems to leverage the fundamental principles of the described method.
The recent press release from Apple, which details the 3D printing process for the Apple Watch Series 11 and Ultra 3, corroborates some of iFixit’s findings. iFixit highlights several advantages of the 3D printing technique used in the iPhone Air. These include reduced overheating of surrounding materials, prevention of warping and discoloration, and a decrease in energy and material waste during production.
Despite the excitement surrounding Apple’s use of 3D printing in its devices, iFixit notes that the implications for repairability remain limited. The company’s analysis indicates that the current approach to 3D printing does not facilitate the sort of ‘print-at-home’ capabilities that consumers might hope for. Additionally, iFixit scrutinizes Apple’s claim that the iPhone Air is constructed with “aerospace grade” titanium, pointing out that this designation does not correspond to a recognized titanium grade.
The exploration of Apple’s 3D printing techniques highlights the company’s commitment to innovation while raising questions about the future of repairability in their products. As the technology evolves, it remains to be seen how these advancements will influence consumer experiences and the sustainability of electronic devices.
For readers interested in the details of Apple’s manufacturing processes, iFixit’s examination offers valuable insights into the intersection of technology and engineering, as well as the potential implications for the broader industry.