Recent scientific advancements have unveiled remarkable insights into various fields, ranging from the genetic makeup of the enigmatic “vampire squid” to the identification of a new tick-borne disease that could affect humans. This week, researchers reported significant findings that not only deepen our understanding of evolutionary biology but also shed light on pressing health concerns.
Rejuvenating Aging Brain Cells
A study led by neuroscientist Benjamin Deneen has shown that boosting a protein known as Sox9 in the brains of mice can activate clean-up cells, effectively reversing signs of cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Deneen noted, “Most current treatments focus on neurons or try to prevent the formation of amyloid plaques. This study suggests that enhancing astrocytes’ natural ability to clean up could be just as important.” This research offers a promising avenue for developing therapies aimed at cognitive health.
Insights into Frailty and Age
Canadian scientists have pinpointed a significant “tipping point” around the age of 75 at which frailty begins to dominate health outcomes for individuals. Their study indicates that both health setbacks and recovery periods lengthen with age, culminating in a tipping point that affects recovery rates. The age range observed for this transition was between 73 and 76 years for both men and women, highlighting the need for focused health interventions in this demographic.
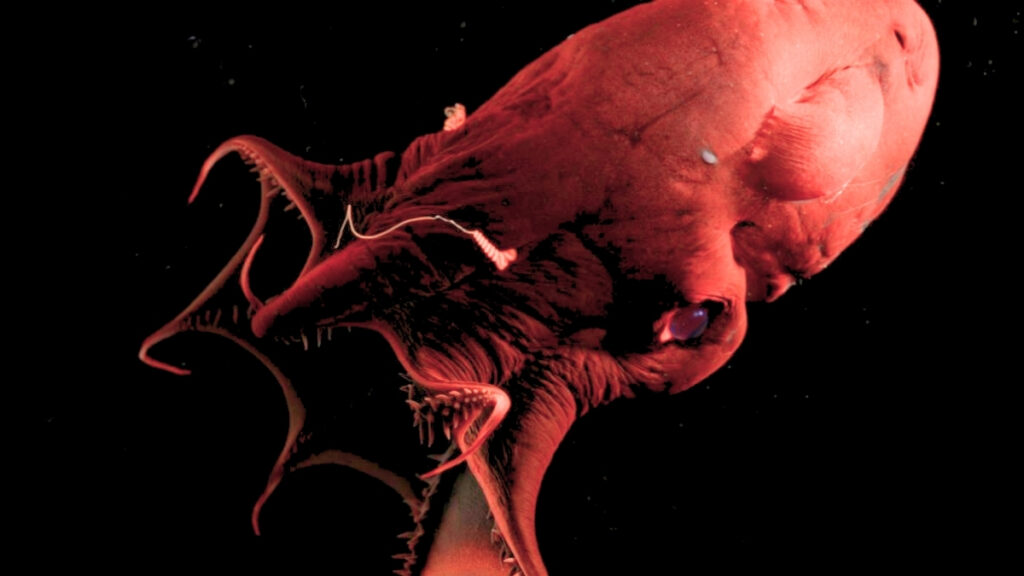
Genetic Secrets of the ‘Vampire Squid’
The mysterious “vampire squid from hell” has revealed its ancient lineage through a comprehensive genomic analysis. Researchers, including genomicist Emese Tóth from the University of Vienna, discovered that this unique creature occupies a crucial evolutionary position between squids and octopuses. Tóth stated, “The vampire squid retains a genetic heritage that predates both squid and octopus lineages, giving us a direct look into the earliest stages of cephalopod evolution.” This finding enhances our understanding of marine biology and evolutionary history.
Dinosaur Tracksite Discovery
A groundbreaking discovery in Bolivia has crowned the world’s largest known dinosaur tracksite, the Carreras Pampa, which boasts nearly 18,000 tracks. Researchers have determined that this site not only shows a remarkable number of tracks but also includes evidence of swimming behaviors. The team noted, “The quality of preservation, the exceptionally high number of tracks, and the diversity of behaviors recorded make the Carreras Pampa tracksite one of the premier dinosaur track sites in the world.” This discovery provides invaluable insights into the lives of dinosaurs.
New Tick-Borne Disease Identified
In a concerning development, scientists in the United States have identified a new tick-borne bacterial disease, named Rickettsia finnyi, which has resulted in fatalities among dogs and poses potential risks to humans. The bacterium was identified through genome sequencing, revealing it as a novel species within the spotted fever group. Researchers are urging caution as they continue to investigate its implications for both canine and human health.
A Galactic Tornado of Galaxies
Astronomers have made a stunning discovery of the longest known rotating structure in the Universe, a filament of galaxies extending 50 million light-years. Physicist Lyla Jung from the University of Oxford described the phenomenon, likening it to a theme park “teacups ride,” where each galaxy spins like a teacup while the larger cosmic filament rotates as a whole. This dual motion provides unique insights into how galaxies acquire their spin from their surrounding structures.
These developments illustrate the dynamic nature of scientific research and its potential to transform our understanding of health, evolution, and the cosmos. As researchers continue to unravel these mysteries, the implications for both human health and our understanding of the universe grow increasingly profound.