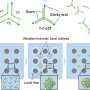
A research group has unveiled an innovative microfluidics technology that significantly improves the production of uniform biomolecular condensates. This development utilizes a simple and cost-effective vibration platform, making it accessible for various applications in biotechnology and molecular biology.
The new technology addresses a critical challenge in the field: achieving consistent and uniform formation of DNA condensates. Traditional methods often lead to variability in size and structure, complicating downstream applications. By employing this vibration platform, researchers can control the conditions under which biomolecules aggregate, resulting in more reliable outcomes.
Implications for Biotechnology
This advancement holds substantial promise for the biotechnology sector. Uniform DNA condensates are essential for applications ranging from drug delivery to genetic engineering. With the ability to produce these structures more consistently, researchers can enhance the effectiveness of their experiments, potentially leading to breakthroughs in therapeutic development.
The research group emphasized that the platform’s affordability could democratize access to advanced techniques previously limited to well-funded laboratories. This is particularly significant for academic institutions and smaller companies that may lack resources for expensive equipment. By lowering the barrier to entry, this innovation could spur a new wave of research and development in the field.
Acknowledgments and Future Directions
The team plans to further explore the potential applications of this technology. Initial tests have shown promising results, but additional studies are needed to fully understand the implications of uniform DNA condensate production across various biological systems.
This breakthrough is the culmination of extensive research and collaboration within the scientific community. The group has collaborated with leading institutions and experts in the field, ensuring that their findings are grounded in rigorous scientific methodology.
As the research progresses, the group aims to publish detailed findings in peer-reviewed journals. Such transparency will allow for broader scrutiny and potential replication by other researchers, further validating the technology’s efficacy.
In summary, the advent of this microfluidics technology represents a significant leap forward in biomolecular research. With its potential to produce uniform DNA condensates efficiently and affordably, it could pave the way for a range of new applications in biotechnology and beyond.







