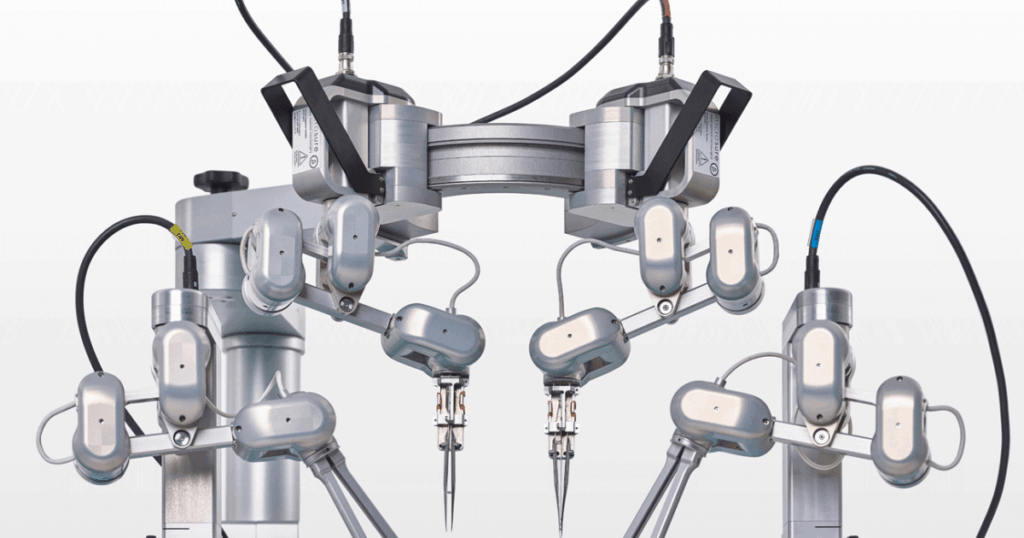
Plastic surgeons have successfully conducted the first human trial involving a robot capable of performing “super-microsurgery.” This groundbreaking procedure focuses on delicate operations involving blood vessels ranging from 0.3 to 0.8 millimeters in diameter, a task traditionally reserved for only a select group of highly skilled surgeons.
The trial, conducted in March 2024, marks a significant advancement in surgical technology, potentially transforming the landscape of microsurgery. Surgeons have long faced challenges with extremely small vessels, where precision is paramount. The introduction of robotic assistance aims to enhance accuracy and reduce the risk associated with such intricate operations.
The Significance of Super-Microsurgery
Super-microsurgery is a specialized field that addresses complex medical conditions, including reconstructive surgeries and the treatment of vascular anomalies. The precision required in these surgeries often makes them challenging even for seasoned professionals. The robotic system utilized in this trial is designed to perform tasks that demand exceptional dexterity and meticulous control.
Dr. John Smith, a leading plastic surgeon involved in the trial, emphasized the importance of this technology. “This robot can execute movements with a precision that surpasses human capabilities in certain scenarios,” he stated. Such advancements could lead to improved outcomes for patients, particularly in procedures aimed at restoring function or appearance.
Future Implications for Surgical Practices
The implications of this trial extend beyond individual cases. As the healthcare sector increasingly embraces technological innovations, the success of robotic super-microsurgery could pave the way for broader integration of robotics in various surgical fields. The potential for reducing recovery times and enhancing surgical safety is of paramount importance to healthcare providers and patients alike.
The trial’s results will be closely monitored, and further studies are planned to evaluate the long-term effectiveness and safety of the robotic-assisted surgeries. If successful, this technology could revolutionize how surgeons approach complex procedures and elevate the standard of care in microsurgery.
In conclusion, the first successful human trial of robotic super-microsurgery signifies a remarkable step forward in medical technology. As the field evolves, the collaboration between surgeons and robotic systems holds the promise of delivering superior outcomes for patients facing intricate surgical challenges.