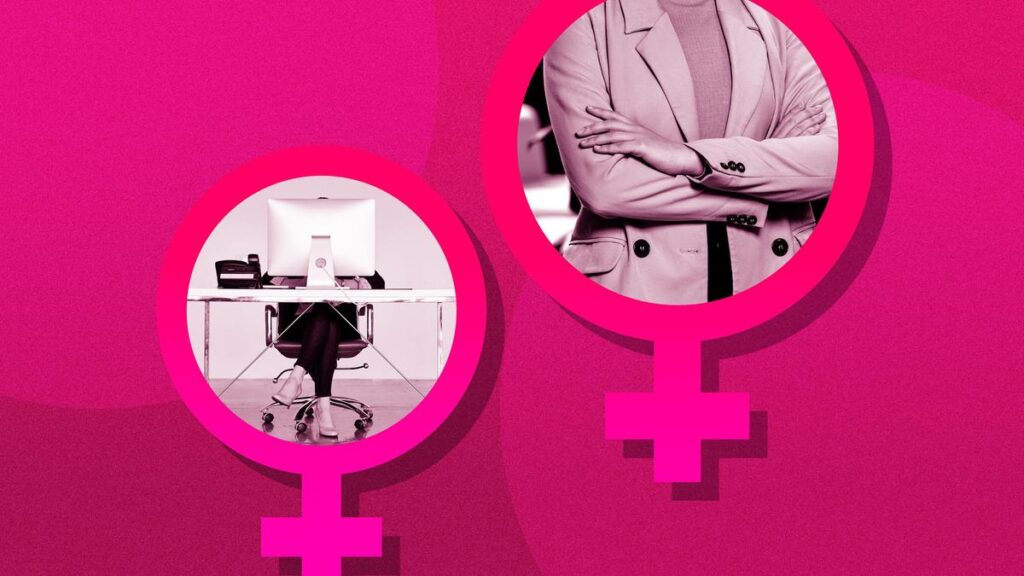
Recent data from the Australian Bureau of Statistics indicates a significant milestone in the Australian job market, with women achieving record participation levels. This surge is attributed to a combination of factors, including evolving public health policies, the rise of remote work, and favorable mortgage conditions.
The latest figures reveal that women’s participation in the workforce has reached an all-time high, breaking previous records set in earlier months. As of March 2024, the employment rate for women stands at over 62%, reflecting a steady increase that has garnered attention from economists and policymakers alike.
Factors Driving Workforce Participation
Several key elements have contributed to this remarkable trend. The ongoing adjustments in public health measures have allowed workplaces to adapt more flexibly to the needs of their employees. Many organizations have embraced a hybrid model, enabling women to balance work and family commitments more effectively.
The rise of work-from-home (WFH) arrangements has proven particularly beneficial, providing women with the opportunity to manage professional responsibilities alongside domestic duties. This shift has been crucial, especially for those with childcare obligations. According to industry experts, the flexibility associated with remote work has empowered women to remain active in the workforce rather than stepping back during challenging times.
Furthermore, favorable mortgage conditions have enabled many households to stabilize their finances, reducing the economic pressure that often leads to workforce withdrawal. With mortgage rates remaining relatively low, families can better manage their living expenses, which can encourage women to pursue or maintain their careers.
Economic Implications
The implications of this increase in women’s workforce participation extend beyond individual households. Economically, a robust female workforce is essential for sustaining growth and innovation within various sectors. As women take on more roles in traditionally male-dominated industries, such as technology and finance, they bring diverse perspectives that can lead to enhanced problem-solving and creativity.
Additionally, this trend may signal a shift in societal attitudes toward gender roles in both the workplace and at home. As more women join the workforce, there is a growing recognition of the importance of equality in career opportunities and the distribution of domestic responsibilities.
While the recent data is promising, challenges remain. Issues such as wage disparity and underrepresentation in leadership positions continue to affect women’s experiences in the workplace. Advocates emphasize the need for ongoing efforts to address these disparities, ensuring that the gains made do not only reflect participation rates but also equitable treatment and opportunities.
As Australia moves forward, the increasing presence of women in the workforce is a positive indicator of economic resilience and societal progress. The combination of supportive policies, flexible work arrangements, and favorable economic conditions will be crucial in maintaining this momentum.