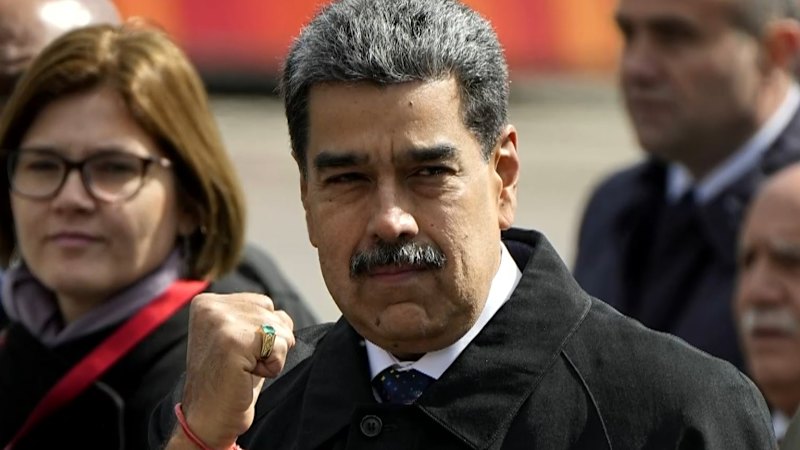
The trajectory of Nicolás Maduro, who transitioned from a unionized bus driver to the President of Venezuela, reflects a complex narrative of political ascent, democratic erosion, and economic turmoil. His leadership, which began in 2013, has been marked by a significant decline in the country’s democratic institutions and a catastrophic economic collapse, culminating in his recent capture by U.S. authorities.
Maduro’s journey to power began during the presidency of Hugo Chávez, where he served as the Minister of Foreign Affairs. Following Chávez’s death in March 2013, Maduro assumed the presidency after winning a contested election. His administration quickly faced allegations of authoritarianism, with the National Assembly and other political institutions increasingly undermined.
Under Maduro’s rule, Venezuela’s economy spiraled downward, exacerbated by falling oil prices and mismanagement. The country, once a thriving oil exporter, witnessed inflation rates soaring to over 3,000% in 2020, making basic goods increasingly inaccessible to the majority of its citizens. The International Monetary Fund labeled Venezuela one of the most severe economic crises in modern history.
As opposition to his rule grew, Maduro employed various tactics to maintain control, including the suppression of protests and the jailing of political opponents. In 2019, opposition leader Juan Guaidó declared himself interim president, a move that received backing from several nations, including the United States. This led to further political unrest and a deepening humanitarian crisis, with millions fleeing the country in search of better living conditions.
In a dramatic turn of events, Maduro’s reign faced a significant challenge as U.S. authorities captured him in early 2023. The charges against him included drug trafficking and corruption, which he has consistently denied. His capture marks a pivotal moment in Venezuelan politics, raising questions about the future of the nation in the wake of his leadership and the ongoing struggle for democracy.
The implications of Maduro’s downfall extend beyond Venezuela. It prompts discussions about U.S. intervention in foreign politics and the effectiveness of sanctions imposed on the regime. As the country grapples with its future, the international community watches closely, considering potential pathways to restore democratic governance and address the significant humanitarian needs of the Venezuelan people.
Maduro’s life story serves as a stark reminder of the fragility of democratic institutions and the profound impacts of leadership on a nation’s trajectory. The challenge ahead will be navigating the complexities of rebuilding amidst a history marked by division and struggle.