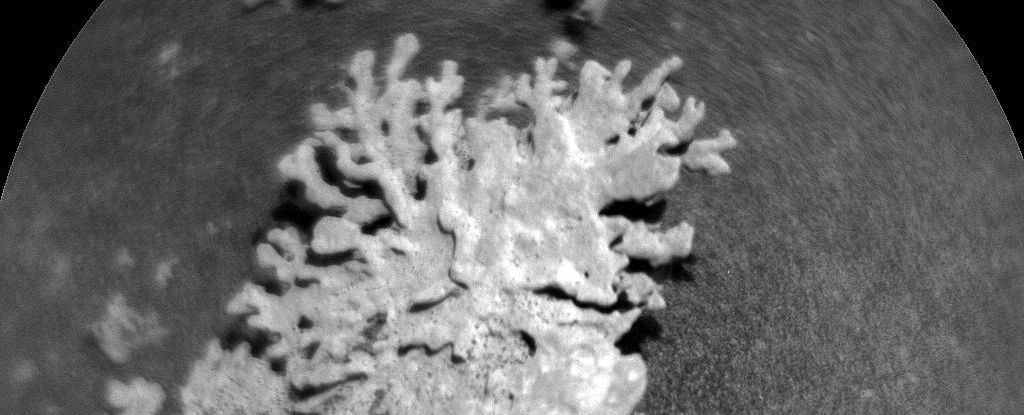
The Curiosity Rover has made an intriguing discovery in the Gale Crater on Mars, unearthing a small rock formation that bears a striking resemblance to branch corals typically found in Earth’s oceans. Measuring just a few centimeters across, this fascinating specimen highlights the similarities in geological processes across different planetary environments, despite Mars lacking surface oceans today.
The formation is not coral or fulgurite—minerals fused by lightning strikes—but rather a remnant of a once-wet Martian environment. According to NASA scientists, water that seeped through cracks in the bedrock carried dissolved minerals, which were deposited as the water drained away. Over time, these mineral concentrations dried and hardened, taking on the shape of the cracks they filled.
In contrast to Earth, Mars experiences intense dust storms that can envelop the planet for extended periods. These storms sculpt the Martian surface through powerful erosion. As a result, formations like this coral-like rock respond variably to the abrasive forces of wind and sand. For this particular structure, the surrounding matrix of sedimentary material was eroded away, leaving behind only the mineral deposits that filled the cracks—an inverse of its original form.
Curiosity’s Ongoing Exploration
Curiosity has been actively exploring the Martian landscape since its landing in August 2012. It has encountered numerous unusual rock formations, including spindly spires and a rock that resembles a flower. Other notable discoveries include a bubbly rock akin to frogspawn and a formation resembling a shrunken face, showcasing the diverse and often bizarre geological features that characterize the Martian terrain.
The discovery of this coral-like rock further emphasizes the importance of studying Mars’ geological history. As scientists continue to analyze these formations, they provide valuable insights into the planet’s past, particularly regarding the presence of water and the environmental conditions that once existed.
The ongoing research conducted by the Curiosity Rover not only broadens our understanding of Mars but also fosters curiosity about the potential for life in other parts of the universe. Each new finding fuels the imagination and inspires continued exploration of our neighboring planet.
In summary, this latest discovery is not just a captivating rock; it serves as a reminder of the intricate processes that shape celestial bodies. The ongoing efforts of the Curiosity Rover contribute significantly to our understanding of Mars, paving the way for future missions and discoveries.