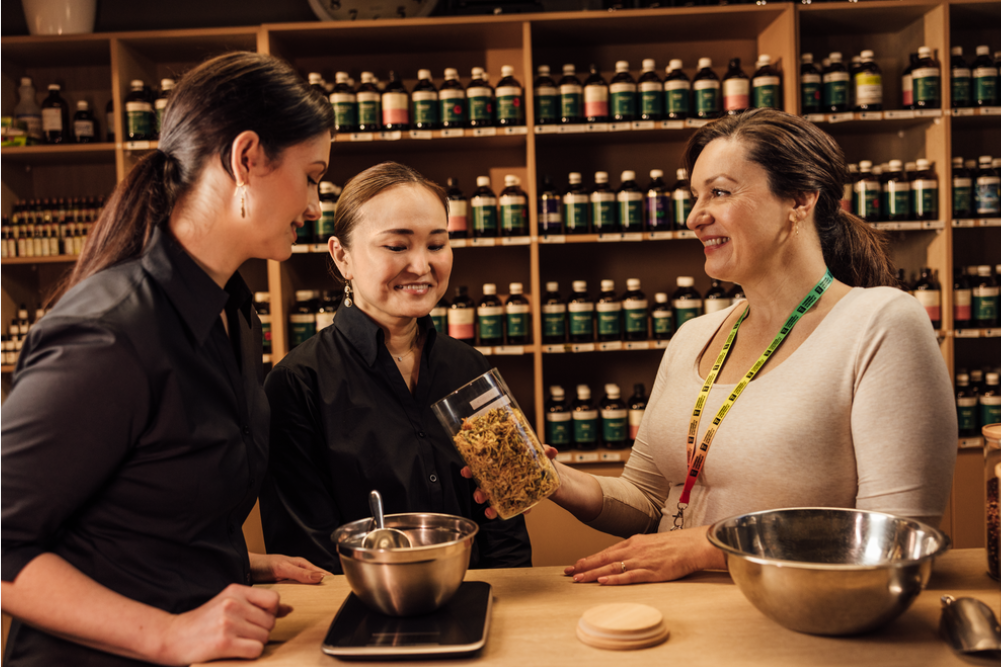
Western herbal medicine has a long-standing tradition that draws from ancient practices in Greece, Rome, and Europe. This holistic approach to health continues to flourish today, leveraging centuries of knowledge and the integration of medicinal plants from diverse cultures. As the interest in herbal remedies grows, certain herbs have emerged as particularly impactful. Here, we explore five key medicinal herbs widely used in Western herbal medicine.
Turmeric: The Golden Anti-Inflammatory
Turmeric, known scientifically as Curcuma longa, has gained a reputation for its vibrant yellow hue and powerful anti-inflammatory properties. Historically utilized as a spice, it plays a significant role in herbal treatment strategies for various inflammatory conditions.
What it does: Turmeric is effective in reducing inflammation, which can benefit individuals suffering from conditions affecting the joints and respiratory systems. Some studies suggest that it may also offer neuroprotective benefits, potentially safeguarding nerves from damage associated with diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Tips: Since the active component, curcumin, is poorly absorbed, many supplements focus on enhancing its bioavailability. Individuals interested in turmeric should consider products designed for better absorption, as effectiveness can vary.
Ashwagandha: Resilience Through Adaptation
Another powerhouse in herbal medicine is Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera), hailed as an adaptogen. This herb, rooted in Ayurvedic traditions, has gained immense popularity for its ability to bolster resilience against stress and illness.
What it does: Ashwagandha helps optimize nerve and hormone function, aiding individuals in adapting to stress. It is particularly beneficial for those recovering from significant health challenges.
Tips: The rising demand for Ashwagandha has led to inconsistencies in product quality. Consumers should ensure they choose extracts from the root rather than the leaf to maximize efficacy.
Chamomile: The Calming Classic
Famed for its soothing qualities, Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla) is a staple in both European and Middle Eastern herbal traditions. Its versatility makes it an essential herb for various applications.
What it does: Chamomile is renowned for its ability to calm nerves and improve sleep quality, making it a popular choice for those feeling anxious. Additionally, it alleviates digestive issues and inflammation, providing relief from stomach discomfort.
Tips: For optimal benefits, chamomile is best consumed as a tea. Covering the cup while brewing helps retain the essential oils that contribute to its therapeutic effects.
Olive Leaf: Nature’s Immune Support
The use of Olive leaf (Olea europaea) dates back to the 19th century, when British botanist Daniel Hanbury documented its use for treating fevers and malaria. Earlier, Spanish doctors had recognized its potential.
What it does: Research indicates that olive leaf may help reduce the risk of viral infections and alleviate symptoms by lowering inflammation and fever. Furthermore, it supports cardiovascular health, with studies showing its effectiveness in lowering blood pressure.
Tips: Consumers should choose olive leaf extracts carefully, as not all products contain adequate levels of oleuropein, the active compound. Look for products that provide at least 75 mg of oleuropein per daily dosage.
Ginkgo: The Brain Booster
Known as the Maidenhair Tree, Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) is the last surviving member of its botanical family, cultivated in China for thousands of years. Despite limited historical use in Traditional Chinese Medicine, it gained prominence in the 1970s through research by German scientist Willmar Schwabe III.
What it does: Ginkgo supports circulation, particularly to the extremities and brain, and may enhance cognitive function. Some studies suggest it could be beneficial for individuals experiencing depression or early cognitive decline.
Tips: Due to its popularity, Ginkgo products can vary significantly in quality. Purchasing products from reputable sources, particularly from regions with stringent regulations like Australia, can help ensure effectiveness.
In summary, Western herbal medicine offers a rich, natural approach to health that complements conventional medical treatments. The herbs discussed here are time-tested remedies, supported by both tradition and modern research.
Before beginning any herbal regimen, it is crucial to consult with a qualified herbalist or naturopath, especially for those on medications or with existing health conditions. For those considering a career in this field, more information can be found at Torrens University Australia, which offers a Bachelor’s degree in Naturopathy and Western Herbal Medicine.
Article by Ian Breakspear, Senior Learning Facilitator – Naturopathy & Western Herbal Medicine at Torrens University Australia.