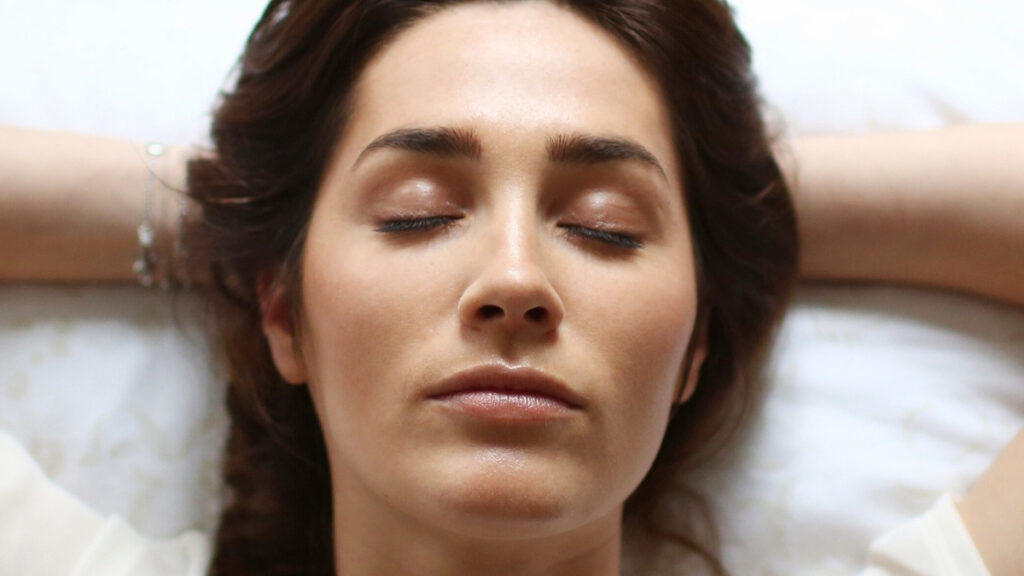
A recent meta-analysis conducted by researchers at Harbin Sport University in China has found that practicing high-intensity yoga significantly improves sleep quality. The study reviewed data from 30 randomized controlled trials involving over 2,500 participants with sleep disturbances. These findings suggest that yoga outperforms other forms of exercise, including walking and resistance training, in enhancing sleep over the long term.
According to the analysis, engaging in high-intensity yoga for less than 30 minutes twice a week serves as the most effective antidote for poor sleep. Participants reported positive results within as little as 8 to 10 weeks. The study also indicated that walking was the second most beneficial physical activity for sleep improvement, followed by resistance exercises.
Contrasting Findings with Previous Research
These conclusions contrast with a 2023 meta-analysis that suggested aerobic or mid-intensity exercises performed three times a week were the most effective for improving sleep quality in individuals experiencing sleep disturbances. Notably, one study within that review acknowledged that yoga had a more pronounced positive effect on sleep outcomes compared to other exercise types. This variation could be attributed to the challenges in categorizing yoga as either aerobic or anaerobic, given its diverse techniques and intensity levels.
Despite the promising results, the recent meta-analysis did not clarify the specific mechanisms by which yoga improves sleep. Several hypotheses exist, including the possibility that yoga enhances heart rate and muscle activation while also regulating breathing. Research indicates that breath control can stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which plays a crucial role in relaxation and digestion. Additionally, some studies propose that yoga may influence brainwave activity, potentially leading to deeper sleep.
The Need for Caution in Interpretation
While the evidence strongly supports the notion that exercise positively impacts sleep, the study’s authors caution against overgeneralizing the findings. “Caution should be exercised when interpreting findings from studies on sleep disturbances, given the limited number of studies included and the unique characteristics of the sleep disturbances population,” the researchers warned.
It is essential to recognize that every individual has unique needs when it comes to addressing insomnia or other sleep-related issues. High-intensity yoga represents one of many options available for those seeking to improve their sleep quality. The study was published in the journal Sleep and Biological Rhythms, with an earlier version released in August 2025.
As research continues to explore the relationship between exercise and sleep, it remains clear that no single solution exists for everyone. Individuals may need to experiment with various forms of physical activity to find the best fit for their personal health and well-being.