Recent announcements from two new partners of NextGenNK reveal significant progress in the field of natural killer (NK) cell-based immunotherapies. These advancements encompass both clinical development and translational research aimed at enhancing cancer treatment efficacy.
Coeptis Therapeutics has obtained worldwide rights to the next-generation GEAR™ Cell Therapy Platform. This platform includes the establishment of a new subsidiary, GEAR Therapeutics, which will focus on advancing GEAR-modified NK cells towards first-in-human cancer studies. The primary goal of this initiative is to augment the effectiveness of antibody-based cancer therapies while minimizing NK cell fratricide. This reduction could lead to better clinical outcomes for patients undergoing treatment.
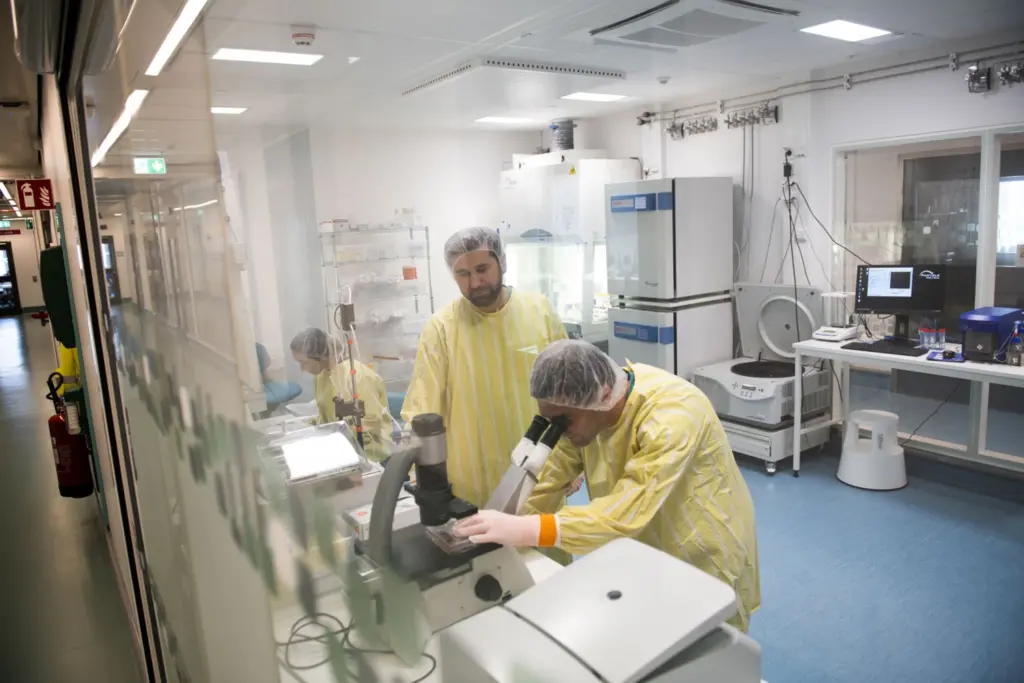
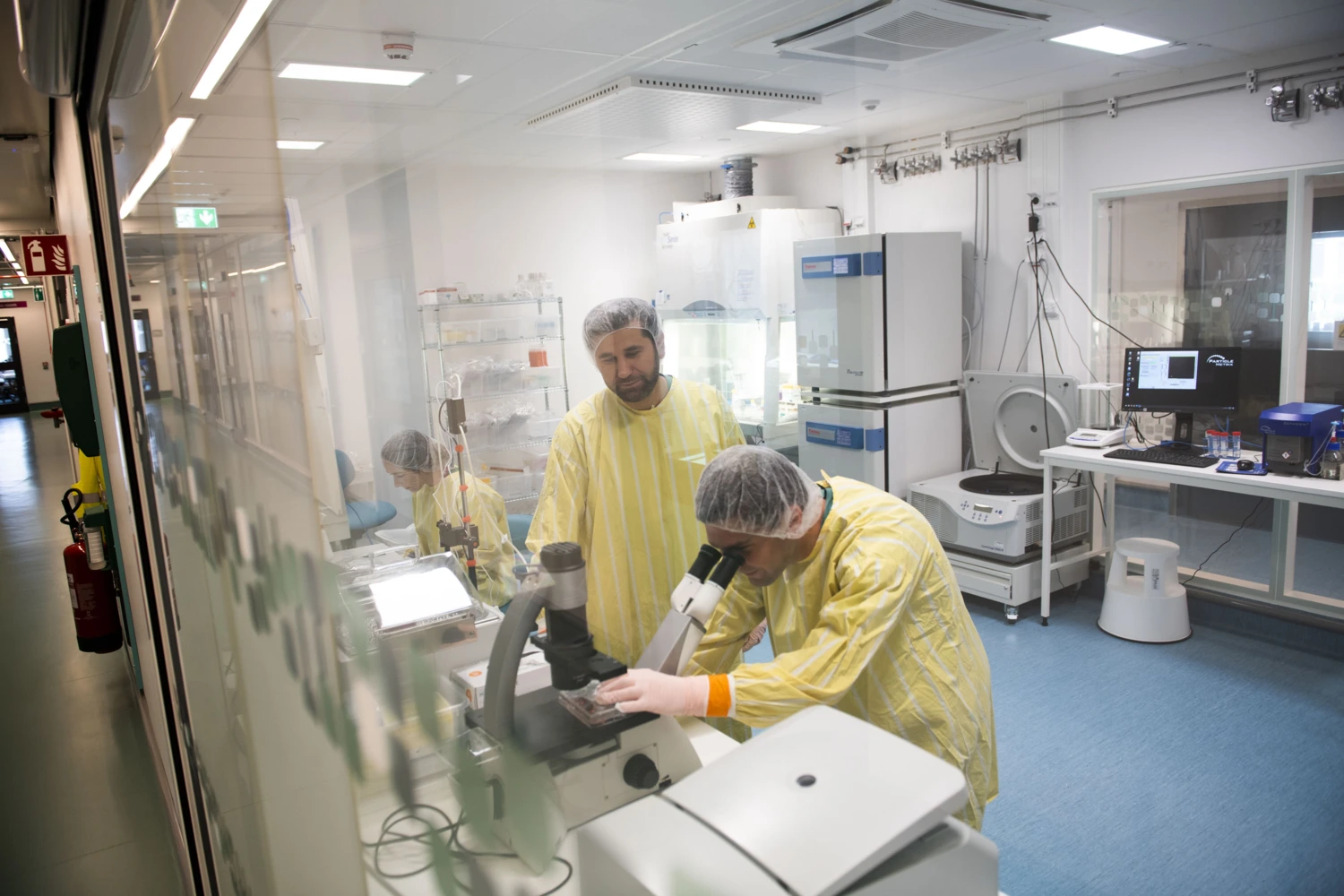
In a parallel effort, Karolinska Institutet and Cellply have initiated a collaboration that leverages Cellply’s VivaCyte platform. This partnership aims to bolster translational NK cell research by characterizing NK cells at the single-cell level and discovering critical biomarkers. These efforts are designed to expedite the development of more effective NK-based therapies, potentially transforming the landscape of cancer treatment.
The focus on NK cells is noteworthy, as these immune cells play a crucial role in identifying and destroying cancerous cells. By refining the characteristics of NK cells and uncovering new biomarkers, researchers hope to enhance the precision and effectiveness of immunotherapies.
Both collaborations highlight an increasing commitment to advancing cancer treatment through innovative research and technology. As the landscape of immunotherapy evolves, partnerships like these signify important steps toward realizing the full potential of NK cell therapies.
As these initiatives progress, they will be closely monitored by the medical community and stakeholders in the biopharmaceutical sector. The outcomes of these research efforts could have significant implications for the future of cancer treatment, offering hope to patients worldwide.