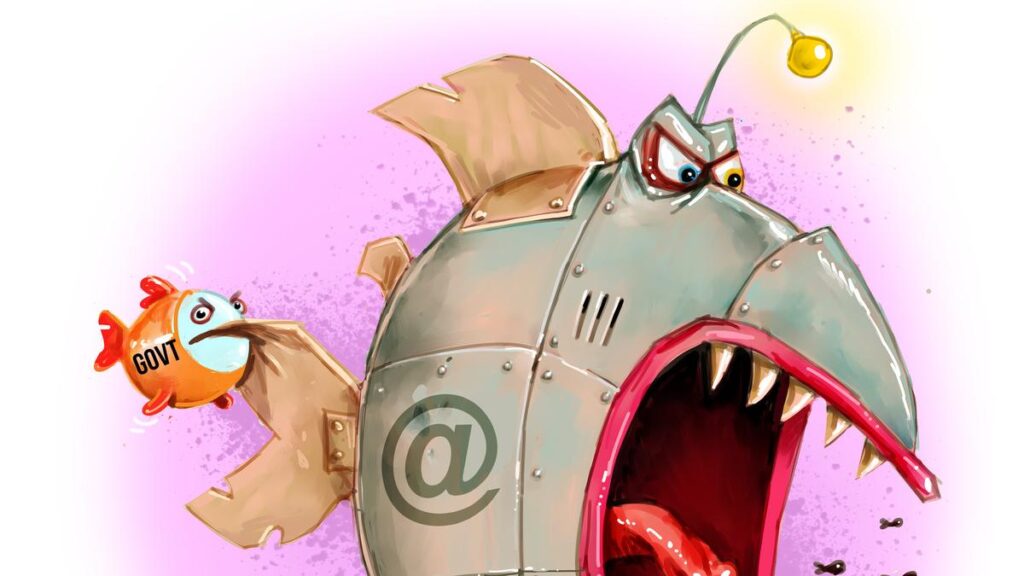
Non perfect Government Internet ban Illustration: Don Lindsay
Legislation aimed at restricting social media access for individuals under the age of 16 has been introduced, sparking discussions about its effectiveness and potential impact. While experts acknowledge the law’s imperfections, they assert it may represent a crucial step in protecting children from harmful online influences.
This new law, proposed in October 2023, targets social media platforms that cater to young audiences. Its primary aim is to limit exposure to inappropriate content and mitigate risks associated with harmful algorithms that can exploit children’s vulnerabilities. Mark Riley, a prominent commentator on social media policies, describes the law as “clunky, flawed and late,” yet stresses its importance given the current digital landscape.
The legislation seeks to impose stricter age verification processes on social media companies. These measures are expected to enhance online safety for minors by ensuring that users under the age of 16 cannot easily access platforms that may expose them to detrimental content. Despite concerns regarding the practicality of enforcing such regulations, proponents believe the law could significantly reduce children’s risks online.
As technology continues to evolve rapidly, the urgency of implementing protective measures grows. Algorithms designed to capture attention can lead children down potentially harmful paths. Riley emphasizes the need for timely interventions to safeguard young users from the next wave of digital threats.
Critics of the legislation have pointed out its limitations, arguing that current technology may not adequately support the proposed age checks. There are also fears that this law may not fully address the complexities of online interactions. Nevertheless, supporters remain optimistic about its potential to inspire future regulatory frameworks that can adapt to fast-changing online environments.
In the broader context, this law aligns with recent efforts by various governments and organizations to prioritize children’s online safety. The European Union, for instance, has been working on comprehensive guidelines to protect minors in the digital space. Such initiatives underscore a growing global awareness of the challenges children face online and the need for concerted action.
While the law is not without its challenges, it may provide a necessary foundation for future legislation aimed at enhancing children’s safety on social media platforms. The balance between protecting young users and allowing them to engage with technology remains a complex issue, but the introduction of this law marks a significant step in the right direction.
As discussions about the implications of social media use continue, this legislation will likely serve as a litmus test for how well governments can protect vulnerable populations in an increasingly digital world. The hope is that, despite its flaws, this law will pave the way for more effective measures that can adapt to the ever-changing landscape of online interactions.