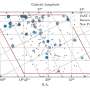
Astronomers from Nanjing University in China have made a significant breakthrough in the field of astrophysics by identifying 19 new pulsars. This discovery was achieved through a meticulous analysis of archival data from the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), which has been instrumental in radio astronomy. The findings were shared on January 5, 2024, on the pre-print server arXiv.
Pulsars, which are highly magnetized rotating neutron stars that emit beams of electromagnetic radiation, are among the most fascinating astronomical objects. The recent analysis highlights the potential of previously collected data to yield new insights into the universe. The researchers focused on data that had not been fully explored in earlier studies, revealing these 19 pulsars that had eluded detection.
The significance of this discovery lies not only in the number of new pulsars identified but also in the techniques employed. Utilizing advanced data analysis methods, the team has underscored the effectiveness of the FAST telescope in uncovering celestial phenomena. The telescope’s vast collecting area allows it to capture faint signals, making it an ideal instrument for such research.
With this discovery, the total number of known pulsars has increased, contributing to our understanding of stellar evolution and the fundamental properties of matter under extreme conditions. The implications of these findings could enhance our knowledge of gravitational waves and neutron star collisions, which are crucial for understanding the fabric of the universe.
Researchers at Nanjing University are now looking ahead, eager to explore further opportunities for pulsar detection. The team plans to continue analyzing FAST data to uncover even more pulsars and deepen their study of these intriguing objects.
In summary, the identification of 19 new pulsars by astronomers at Nanjing University marks a notable achievement in astrophysics. As the research community continues to leverage advanced observational technologies, the universe reveals more of its secrets, one pulsar at a time. The ongoing work promises to yield further discoveries, potentially reshaping our understanding of the cosmos.






