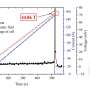
A research team from the High Magnetic Field Laboratory at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has achieved a significant milestone in the field of superconductivity. Led by scientists Kuang Guangli and Jiang Donghui, the team developed a “pocket-type” high-temperature superconducting (HTS) coil, which reached a record combined magnetic field strength of 44.86 tesla.
This breakthrough represents a major advancement in material science and has potential implications for various applications, including particle accelerators, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and energy storage systems. The innovation of a “pocket-type” design also suggests enhanced portability and practical usability, addressing some of the limitations found in traditional superconducting coils.
The achievement was made possible through rigorous research and development efforts, leveraging advanced materials and innovative engineering techniques. The team utilized unique fabrication methods that allow for the compact construction of the coil while maintaining exceptional performance under high magnetic field conditions.
Significance of the Achievement
The attainment of 44.86 tesla is noteworthy, as it surpasses previous records in high-temperature superconductivity. This level of magnetic field strength is critical for numerous high-tech applications, particularly in experimental physics and medical technology. The ability to produce such powerful magnetic fields could lead to more efficient and effective technologies, particularly in the fields of energy and healthcare.
Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity without resistance at certain temperatures. The development of high-temperature superconductors has opened new avenues for research and application, as they operate at temperatures that are more easily achievable than traditional superconductors, which often require extreme cooling.
The implications of this research are vast. For instance, in the medical field, enhanced superconducting coils could improve the resolution and effectiveness of MRI machines, potentially leading to better diagnostics. In energy applications, these coils could facilitate the development of more efficient energy storage systems, contributing to advancements in renewable energy technologies.
Future Directions
Following this remarkable achievement, the research team plans to further explore the applications of their “pocket-type” HTS coil. Future projects will likely focus on optimizing performance and expanding the coil’s usability in real-world scenarios. Collaborations with industry partners may also be on the horizon, allowing for the translation of this research into practical technologies.
The work done by Kuang Guangli and Jiang Donghui, along with their colleagues, underscores the importance of continued investment in scientific research and development. As the demand for advanced materials and technologies grows, innovations like this will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of various industries.
This achievement not only showcases the capabilities of Chinese researchers but also contributes to the global body of knowledge in superconductivity. As the team continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, the scientific community and industries around the world will be watching closely for further developments.






