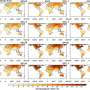
A recent study conducted by the University of California, Berkeley, has demonstrated that global warming is causing significant increases in day-to-day temperature fluctuations. This phenomenon, described as a “climate roller coaster,” poses a serious risk to human health as populations are increasingly exposed to extreme temperature changes.
The research indicates that these rapid temperature swings are not merely isolated incidents but rather a growing trend linked to climate change. As global temperatures rise, the volatility in daily weather patterns has intensified, leading to more frequent and sharp contrasts between temperature extremes. This trend has been observed across various regions, affecting communities worldwide.
Implications for Public Health
The implications of these temperature shifts are profound. Extreme temperature variations can exacerbate existing health issues, increase the risk of heat-related illnesses, and even contribute to higher mortality rates. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions, are particularly at risk.
According to the study, the health impacts associated with these temperature fluctuations could lead to increased healthcare costs and demand for medical services. This places additional strain on health systems already grappling with the effects of climate change. Public health officials are urged to prepare for these changes and implement strategies to mitigate the associated risks.
The study’s findings underscore the urgent need for global awareness and action regarding climate change. With the World Health Organization (WHO) emphasizing the link between climate and health, governments and organizations must prioritize policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices.
Understanding the Climate Roller Coaster
The term “climate roller coaster” aptly captures the unpredictable nature of today’s weather patterns. The research highlights that fluctuations can lead to both unseasonably warm and cold days, often within short timeframes. For example, a region might experience unseasonably high temperatures one day, followed by a sudden drop the next.
These erratic changes challenge traditional weather forecasting methods and complicate agricultural planning, energy consumption, and water resource management. Farmers, for instance, face difficulties in anticipating planting and harvesting times, which can affect crop yields and food security.
In conclusion, the study from the University of California, Berkeley, serves as a critical reminder of the far-reaching consequences of global warming. As temperature swings become more pronounced, the need for comprehensive strategies to protect public health and adapt to changing climate conditions is more pressing than ever. Addressing these challenges will require collaboration between governments, health organizations, and communities worldwide to foster resilience and safeguard health in an increasingly volatile climate.






