Astronomers have identified a third interstellar object in our Solar System, designated 3I/ATLAS (C/2025 N1 ATLAS). Detected on July 1, 2025, by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) in Rio Hurtado, Chile, this comet has ignited significant scientific interest. Following the discovery of the first two interstellar objects, ‘Oumuamua in 2017 and 2I/Borisov in 2019, the arrival of 3I/ATLAS has prompted discussions about potential missions to study such enigmatic celestial visitors.
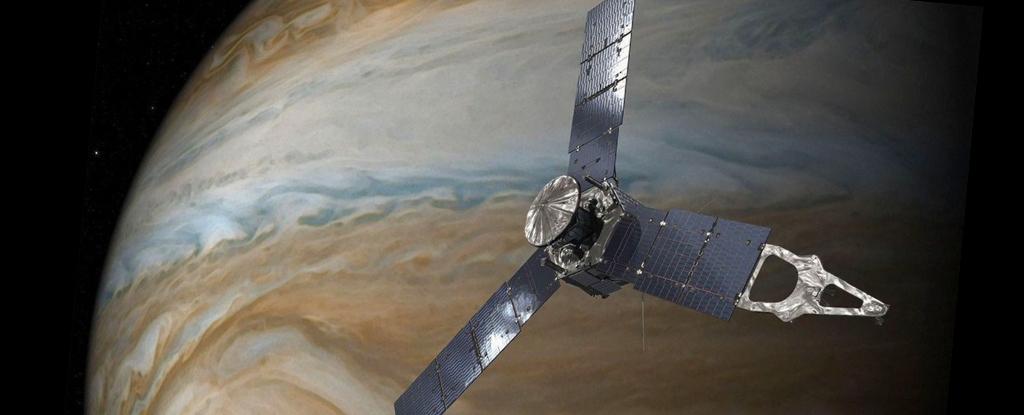
A recent study led by Prof. Abraham Loeb from Harvard University proposes an innovative approach to investigate 3I/ATLAS. The study suggests that NASA’s Juno probe, currently studying Jupiter, could intercept this interstellar comet as it approaches the gas giant on March 16, 2026. This mission could provide valuable insights into one of the most mysterious classes of objects in the universe.
Potential Intercept and Scientific Opportunities
The analysis indicates that the Juno spacecraft can shift its trajectory to meet 3I/ATLAS at its closest approach to Jupiter. This maneuver would involve a thrust application of 2.675 kilometers per second on September 14, 2025. The opportunity for Juno to intercept 3I/ATLAS is significant due to its projected distance of about 53.6 million kilometers (approximately 33.25 million miles) from Jupiter at that time.
Prof. Loeb, who is also the Director of the Institute for Theory and Computation and the Galileo Project at the Harvard & Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, emphasizes the scientific value of this potential encounter. The study’s co-authors, Adam Hibberd and Adam Crowl, both associated with the UK-based non-profit Initiative for Interstellar Studies (i4is), bring extensive experience in interstellar research and mission design.
The Juno probe’s suite of instruments, including a near-infrared spectrometer and a visible light camera, could be utilized to analyze the composition of 3I/ATLAS. This analysis could yield insights into the conditions present when the object formed, thereby enhancing our understanding of other star systems.
Exploring the Nature of 3I/ATLAS
While the proposed mission is exciting, it is not without its uncertainties. The hypothesis that 3I/ATLAS might represent an artificial object, perhaps a derelict spacecraft, has generated discussion in the scientific community. Prof. Loeb’s previous works, including his paper titled “Could Solar Radiation Pressure Explain ‘Oumuamua’s Peculiar Acceleration?” have gained significant attention, suggesting the possibility of extraterrestrial technology.
In their recent paper titled “Is the Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS Alien Technology?”, the authors acknowledge the intriguing yet speculative nature of their hypothesis. Prof. Loeb points out that while they do not necessarily endorse the idea of 3I/ATLAS being an alien artifact, it warrants serious scientific exploration due to the potential implications for humanity.
Recent observations from the Hubble Space Telescope have raised questions about the size of 3I/ATLAS, estimating its nucleus to be less than 2.8 kilometers (approximately 1.75 miles