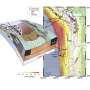
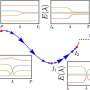
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have developed a groundbreaking method to quantify the hidden energy costs associated with maintaining metabolic pathways. This new approach sheds light on the energy required to sustain specific biochemical processes, such as photosynthesis, while simultaneously preventing alternative processes that could disrupt these essential functions.
Understanding the energy dynamics of metabolic pathways is crucial for various fields, including biology, environmental science, and biotechnology. The research highlights that traditional mechanical physics often overlooks these “costs of life,” which play a vital role in sustaining ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Unveiling the Energy Costs
The study, published in March 2024, provides a detailed analysis of how energy is allocated within cells to maintain specific metabolic functions. For instance, during photosynthesis, plants convert light energy into chemical energy, requiring a significant amount of energy to keep this process active. The researchers emphasize that while the benefits of such processes are often recognized, the hidden energy expenses involved have not been adequately quantified until now.
This novel method allows scientists to measure the energy expenditure in real-time, offering insights into how organisms balance various metabolic functions. The researchers utilized advanced computational models alongside experimental data to develop a comprehensive framework for understanding these energy costs.
Implications for Environmental Science and Agriculture
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest. By quantifying the energy costs of metabolic pathways, the findings can inform more sustainable agricultural practices. Farmers could optimize energy use in crop production by understanding the metabolic requirements of plants. This knowledge could lead to enhanced crop yields and reduced reliance on chemical fertilizers.
Furthermore, the research holds potential for addressing environmental challenges. As climate change impacts agricultural systems, understanding the energy dynamics of photosynthesis and other metabolic processes will be critical in developing resilient crops that can thrive in changing conditions.
The work of the Berkeley researchers represents a significant advancement in the field of metabolic biology. Their innovative method not only enhances our understanding of energy costs but also opens avenues for practical applications that could benefit both agriculture and environmental conservation.
In conclusion, the ability to quantify the hidden energy costs of metabolic pathways marks a notable step forward in biological research. As scientists continue to explore these intricate processes, the potential for positive impacts on food security and ecological sustainability becomes increasingly evident.