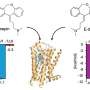
Recent findings have shed light on the complex mechanisms of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), a significant family of proteins that play a critical role in human physiology. These receptors, which recognize hormones, neurotransmitters, and drugs, are instrumental in regulating various bodily functions and are the targets for over 30% of marketed medications. Among them, the histamine H1 receptor (H1R) is pivotal in mediating responses related to allergies, inflammation, and cognitive functions.
Understanding H1R’s Role in Drug Response
The H1R receptor’s influence extends to numerous physiological processes, including vascular permeability and airway constriction. It plays a crucial role in the body’s response to allergens and inflammation. While many antihistamines effectively target H1R, they often exhibit limited therapeutic efficacy, leading researchers to explore new avenues in understanding H1R ligands.
Recent research has focused on how H1R differentiates between two nearly identical drug molecules. This differentiation is essential for improving drug design and efficacy. Scientists are now investigating the structural and functional properties of H1R, aiming to identify specific characteristics that enable it to distinguish between similar compounds. This approach could enhance the development of more effective antihistamines and other treatments.
Implications for Future Drug Development
Understanding the intricacies of H1R could lead to significant advancements in the pharmaceutical industry. With a better grasp of how H1R interacts with different ligands, researchers can design drugs that are more targeted and effective. This new perspective on H1R ligands could result in therapies that not only alleviate symptoms more effectively but also minimize side effects associated with current antihistamines.
As the research progresses, the implications for patients suffering from allergies and other related conditions could be profound. Enhanced therapeutic options could lead to improved quality of life for many individuals, demonstrating the vital importance of ongoing research in this area. The findings underscore the need for continued innovation in drug design, particularly in the realm of GPCRs.
In summary, the ongoing exploration of GPCRs, specifically the histamine H1 receptor, reveals critical insights into drug efficacy and design. As researchers delve deeper into the mechanisms that govern these receptors, the prospects for developing more effective treatments become increasingly promising.






