Recent advancements in science have brought forth significant findings and policy updates across various fields. These developments include new guidelines for blood pressure management in the United States, the discovery of unusual geological formations in the North Sea, and groundbreaking research into the effects of scents on brain structure.
New Blood Pressure Guidelines Released
The American Heart Association (AHA) and the American College of Cardiology (ACC), alongside other medical institutions, have introduced updated guidelines for managing high blood pressure. Released in March 2024, these guidelines emphasize preventive measures and earlier intervention, reflecting a shift in the approach to cardiovascular health. This revision updates the previous guidelines from 2017, aiming to reduce the incidence of hypertension-related complications.
The comprehensive guidelines provide healthcare professionals with a framework to identify at-risk patients and implement lifestyle changes early. This proactive strategy may lead to improved health outcomes for millions of individuals across the United States.
Unusual Geological Findings in the North Sea
In a remarkable geological discovery, researchers have identified large sections of the seafloor in the North Sea that are positioned ‘upside down.’ This phenomenon involves younger, denser sediment layers sinking beneath older, lighter ones, a process known as stratigraphic inversion. The presence of these vast sand mounds, which rest atop structures called sinkites, marks a significant finding, as such formations have not been reported in such quantities before.
The implications of this discovery extend beyond mere curiosity; understanding these geological processes could provide insights into historical climate changes and geological activity in marine environments.
Brightest Radio Flash Ever Detected
Astronomers have made an astounding discovery with the detection of the brightest radio flash ever observed, originating from a galaxy approximately 130 million light-years away. This phenomenon has been dubbed the RBFLOAT—an acronym for Radio-Brightest Flash of All Time—and is humorously referred to as the Root Beer FLOAT among the scientific community.
Utilizing the CHIME Radio Telescope, researchers captured this unprecedented cosmic event, which opens new avenues for understanding the universe’s most powerful energy sources. The findings highlight the potential for future discoveries in astrophysics and the study of cosmic phenomena.
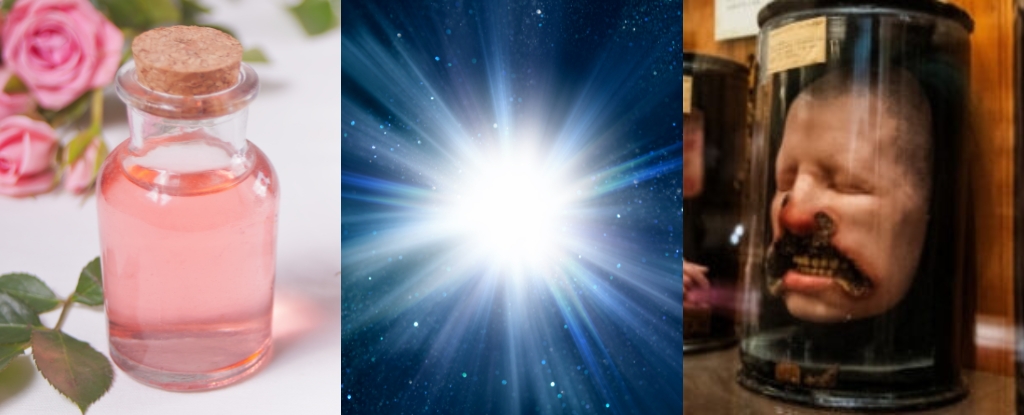
Impact of Scents on Brain Structure
A new study has revealed that wearing rose-scented oil for a month can lead to an increase in brain volume among participants compared to those who did not wear any scent. This research, published by a team of neuroscientists, is the first to demonstrate that continuous inhalation of a scent can alter brain structure.
The implications of this study suggest that sensory experiences, particularly olfactory stimuli, may play a significant role in cognitive health. As researchers continue to explore these connections, the potential applications in mental health and wellness could be substantial.
The Gut-Brain Connection and Insomnia
Emerging research has uncovered a complex relationship between gut microbiota and insomnia. Certain types of gut microbes have been linked to an increased risk of sleep disturbances, while others may help mitigate these issues. This bidirectional relationship indicates that poor sleep can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, potentially creating a feedback loop that exacerbates insomnia.
Understanding this connection could lead to new treatment strategies for those suffering from sleep disorders, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiome for overall well-being.
These recent scientific developments not only highlight the dynamic nature of research but also underscore the interconnectedness of health, environment, and the cosmos. Each finding contributes to a broader understanding of the world and our place within it.